Overview
What is MEV-Boost?
mev-boost is open source middleware run by validators to access a competitive block-building market. MEV-Boost was built by Flashbots as an implementation of proposer-builder separation (PBS) for proof-of-stake (PoS) Ethereum.
With MEV-Boost, validators can access blocks from a marketplace of builders. Builders produce blocks containing transaction orderflow and a fee for the block proposing validator. Separating the role of proposers from block builders promotes greater competition, decentralization, and censorship-resistance for Ethereum.
See also:
Why MEV-Boost?
MEV is a centralizing force on Ethereum. Unattended, the competition for MEV opportunities leads to consensus instability and permissioned communication infrastructure between searchers, block producers, and validators. Access to MEV is even more important in PoS Ethereum, as the planned reduction in block subsidies will make MEV an even larger share of total staking revenue.
Validators running MEV-Boost maximize their staking reward by selling their blockspace to an open market. It is estimated that validators running MEV-Boost can increase staking rewards by over 60%.
How does MEV-Boost work?
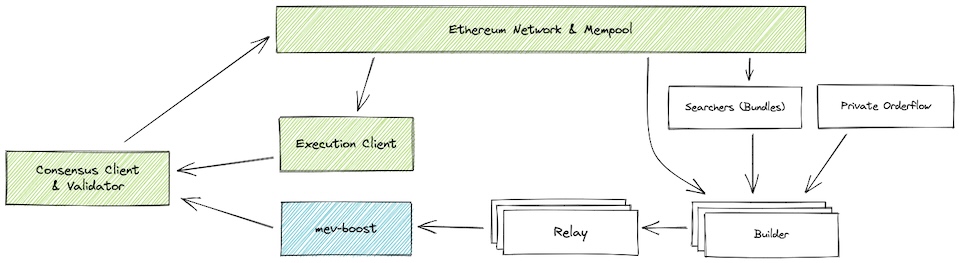
PoS node operators must run three pieces of software: a validator client, consensus client, and an execution client. MEV-boost is a sidecar for the consensus client, a separate piece of open source software, which queries and outsources block-building to a network of builders.
Block builders prepare full blocks, optimizing for MEV extraction and fair distribution of rewards, and send blocks to relays. A single MEV-boost instance can be configured to connect to multiple relays.
Relays aggregate blocks from multiple builders and identify the most profitable block to submit to the block proposer. The proposing validators’ consensus client then propagates the most profitable block received from MEV-boost to the Ethereum network for attestation and block inclusion.